Understanding EventEmitter vs. RxJS in Angular: A Deep Dive
When building applications in Angular, you often need to implement an observer pattern to handle data flows and events. Two common approaches are using EventEmitter and RxJS. In this post, we’ll explore the differences between these two methods, complete with code examples.
EventEmitter
EventEmitter is a simple way to create custom events in Angular, primarily used for parent-child component communication.
Example of EventEmitter
Here’s how you can use EventEmitter in a component:
import { Component, EventEmitter, Output } from '@angular/core';@Component({
selector: 'app-child',
template: `<button (click)="sendData()">Send Data</button>`
})
export class ChildComponent {
@Output() dataEmitter = new EventEmitter<string>(); sendData() {
this.dataEmitter.emit('Hello from Child!');
}
}@Component({
selector: 'app-parent',
template: `<app-child (dataEmitter)="receiveData($event)"></app-child>`
})
export class ParentComponent {
receiveData(data: string) {
console.log(data);
}
}
When to Use EventEmitter
- Simplicity: Ideal for straightforward event handling between components, especially for one-off events.
- Limited Scope: Best when you only need to pass data from child to parent components.
RxJS
RxJS is a powerful library for handling asynchronous data streams. It provides a more robust and flexible approach compared to EventEmitter, especially for complex scenarios.
Example of RxJS
Here’s how to use RxJS with a Subject:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Subject } from 'rxjs';@Component({
selector: 'app-rxjs-example',
template: `<button (click)="sendData()">Send Data</button>`
})
export class RxjsExampleComponent {
private dataSubject = new Subject<string>(); constructor() {
this.dataSubject.subscribe(data => {
console.log(data);
});
} sendData() {
this.dataSubject.next('Hello from RxJS!');
}
}
When to Use RxJS
- Advanced Features: Ideal for handling multiple asynchronous events, such as API calls and user interactions.
- Complex Scenarios: Allows for more complex data manipulation using operators like
map,filter, andmerge. - Multicasting: Supports multiple subscribers sharing the same data stream, providing greater flexibility.
- Error Handling: Offers built-in support for error handling and cancellation.
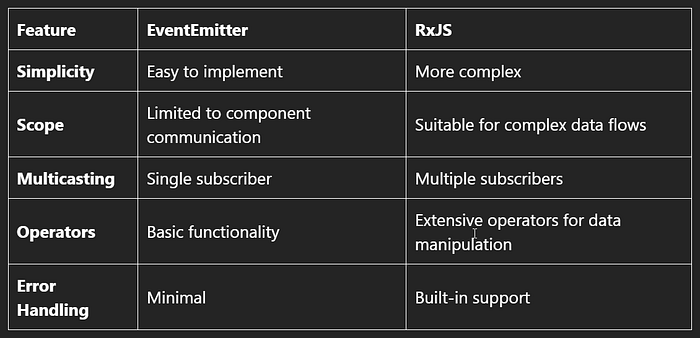
Key Differences
Conclusion
Both EventEmitter and RxJS serve their purposes in Angular applications. Use EventEmitter for simple event handling between components, while RxJS is better suited for complex asynchronous data flows. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right approach for your application's needs. Happy coding!
#angular #eventemitter #rxjs #statemanagement #javascript #frontend #developer